Create new database
To create a new database, right click on the "Databases" node in the left panel in the Management studio. You will get couple of options in the context menu. Select the option 'New Database'.

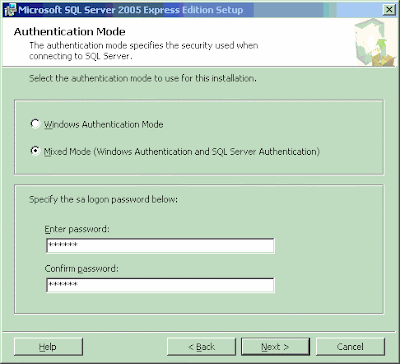
You will get another dialog box where you have to specify few details. The most important one is the database name. In the below screenshot, I have specified the new database name as "MySampleDatabase".

You may notice two other circled fields called "logical name" and "path". When any database is created, there is at least 2 files created in the hard disk. One file is called "Data file" and it has an extension of .MDF. The other file is called "log file" and it has an extension of .LDF by default. The logical names are the internal names used by the SQL Server to represent the data file and logical file. The path represents the physical location of the above files in your hard disk. The default location will be within the Program Files folder. You may change it to your projects folder or any other folder you want. However, the only mandatory entry required fill to create a new database is the database name.